herunterladen
AN-960
APPLICATION NOTE
One Technology Way • P. O. Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Te l: 781.329.4700 • Fax: 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
RS-485/RS-422 Circuit Implementation Guide
by Hein Marais
Rev. 0 | Page 1 of 12
INTRODUCTION
Industrial and instrumentation applications (I&I) require
transmission of data between multiple systems often over
very long distances. The RS-485 bus standard is one of the
most widely used physical layer bus designs in I&I applica-
tions. The key features of RS-485 that make it ideal for use
in I&I communications applications are
• Long distance links—up to 4000 feet.
• Bidirectional communications possible over a single pair of
twisted cables.
• Differential transmission increases noise immunity and
decreases noise emissions.
• Multiple drivers and receivers can be connected on the
same bus.
• Wide common-mode range allows for differences in
ground potential between the driver and receiver.
• TIA/EIA-485-A allow for data rates of up to 10 Mbps.
Devices meeting the TIA/EIA-485-A specifications do not
have to operate over the entire range and are not limited
to 10 Mbps.
The purpose of this application note is to discuss the imple-
mentation of RS-485/RS-422 in an industrial environment.
Applications for RS-485/RS-422 include process control
networks; industrial automation; remote terminals; building
automation, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning
(HVAC), security systems; motor control; and motion control.
TIA/EIA-485-A, the telecommunication industry’s most widely
used transmission line standard, describes the physical layer of
the RS-485 interface and is normally used with a higher-level
protocol, such as Profibus, Interbus, Modbus, or BACnet. This
allows for robust data transmission over relatively long distances.
The RS-422 physical layer is described in TIA/EIA-422-B. The
TIA/EIA-485-A standards are similar to those described in
TIA/EIA-422-B, and the values used to specify the drivers and
receivers in TIA/EIA-485-A standards are specified so that it
can meet both standards.
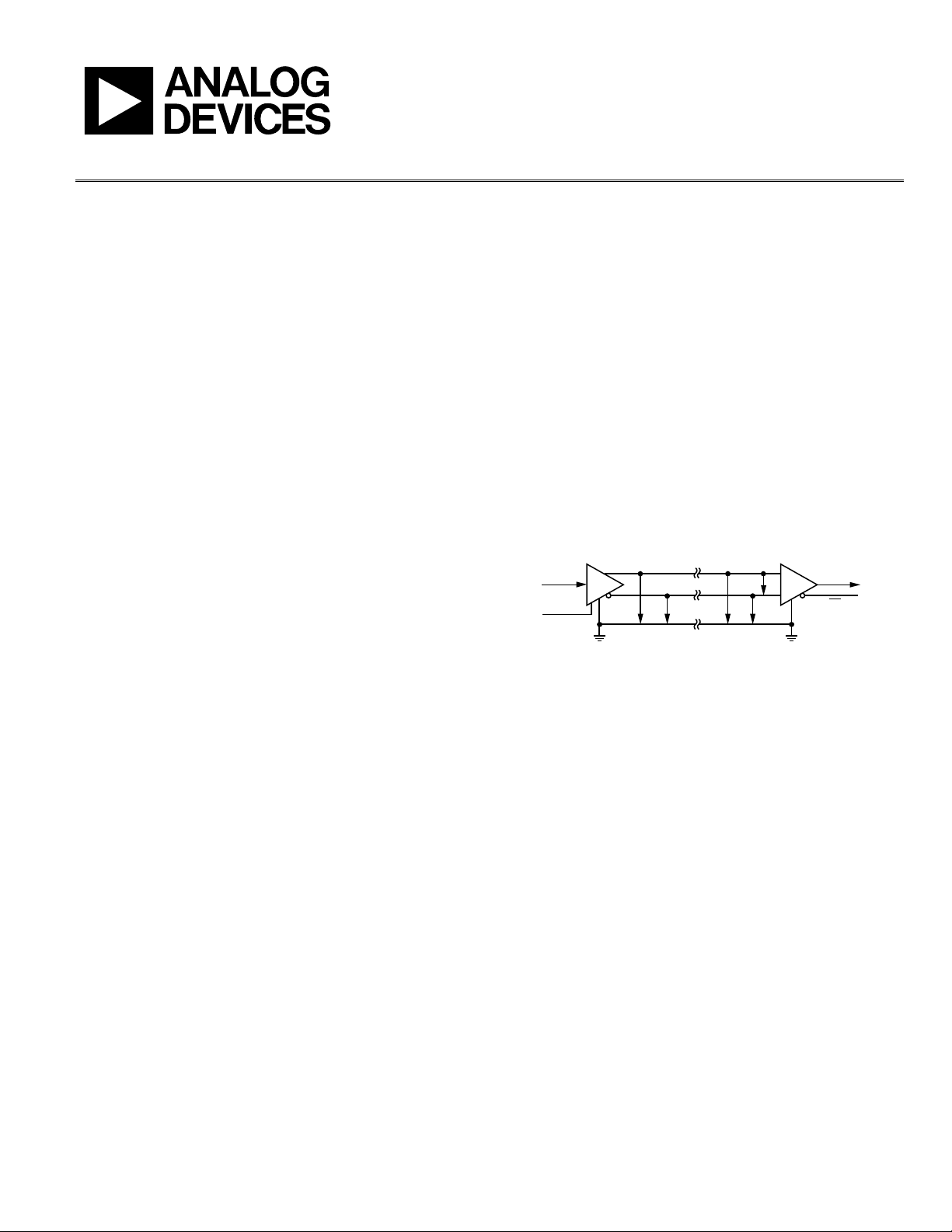
WHY USE DIFFERENTIAL DATA TRANSMISSION?
The main reason why RS-485 can communicate over long
distances is the use of differential or balanced lines. A com-
munication channel requires a dedicated pair of signal lines
to exchange information. The voltage on one line equals the
inverse of the voltage on the other line.
TIA/EIA-485-A designates the two lines in this differential pair
as A and B. Line A is more positive than Line B (V
OA
> V
OB
) on
the driver output if a logic high is received on the input of the
transmitter (DI = 1). If a logic low is received on the input of the
transmitter (DI = 0), the transmitter causes Line B to be more
positive than Line A (V
OB
> V
OA
). See Figure 1.
V
OA
V
IA
V
OB
V
IB
V
OD
B
A
DI
DE
RO
RE
07395-001
Figure 1. Differential Transmitter and Receiver
If Line A is more positive than line B (V
IA
− V
IB
> 200 mV)
on the input of the receiver, the receiver output is a logic high
(RO = 1). If Line B is more positive than Line A (V
IB
− V
IA
>
200 mV) on the input of the receiver, the receiver output is a
logic low (RO = 0).
Figure 1 shows that a differential signaling interface circuit
consists of a driver with differential outputs and a receiver with
differential inputs. This circuit has increased noise performance
because the noise coupling into the system is equal on both
signals. One signal emits the opposite of the other signal and
electromagnetic fields cancel each other. This reduces the
electromagnetic interference (EMI) of the system.
Verzeichnis