herunterladen
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Analog Switches and Multiplexers > APP 745
Keywords: fault-protection, analog switch, CMOS analog multiplexers, overvoltage, zener clamp, parallel
sense, series protection diodes, fault protected switches, analog multiplexer
APPLICATION NOTE 745
Fault-Tolerant Analog Switches
Mar 25, 2001
Abstract: The following discussion describes the advantages of Maxim's new parallel sense fault-
protection architecture over the traditional series-FETs approach.
In certain applications, board designers add circuitry to protect analog-switch inputs from voltages that
exceed the supply rails. When these voltages are present, not only must the switch survive them, but
also—to protect the circuitry downstream from the switch—the voltage from the switch's output must
remain within its supply rails. In addition, the switch must survive a voltage present at its input when the
supplies powering the switch are off, and the downstream circuitry must again be spared voltages that
could cause damage. All of the foregoing not only pertains to analog switches but to analog multiplexers
as well.
These problems (called "faults") are often caused when a switch input is connected inadvertently to a
higher-level voltage. A fault condition can also arise when a system component fails, shorting the high-
voltage supply that powers it to the switch that is connected to it. Yet another situation can also be the
cause: When two or more independent supplies power the switch and its surrounding circuitry, if these
supplies power up in the wrong order, a voltage may be placed on a switch input prior to the switch
supply voltage being powered. Of course, a fix for this last problem is simply to sequence the power
supplies in the correct order. This usually means turning on the positive supply first, followed by the
negative supply, and after that any inputs. Adding diodes between the supplies, so that sequencing the
supplies in a particular order becomes unnecessary, can work too. Power-supply sequencing problems
also show up with switches that have a logic supply in addition to the main supply voltages. If a switch's
logic supply comes up before the main supply, a latch condition can result. Again, all of this applies to
analog multiplexers as well as to analog switches.
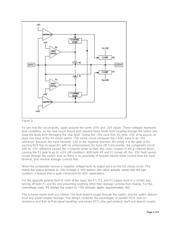
Engineers have often fixed the problems described above by using external resistors to limit the current
that flows into a switch (or a mux) during a fault. Given sufficient circuit-board real estate, this approach
works reasonably well. However, when using this technique, a fault on one switch or mux input causes
inaccuracies on the remaining inputs, which is a problem when it's necessary to retain accurate analog
signals on the nonfaulted lines. Also, a fault voltage can pass through the external resistor and the
switch/mux, causing damage to the downstream circuits. Resistor-diode networks eliminate these
problems, but significantly increase the component count in the process.
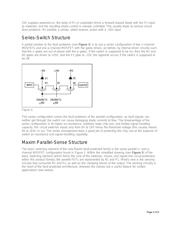
Maxim has developed a new process and architecture that addresses these problems. This new
approach marks a major advance over the three-FETs-in-series technique (described below), because it
allows Rail-to-Rail operation and it demonstrates significantly lower on-resistance. The new technique
uses on-chip sensing circuitry to detect the presence of fault conditions; when the sensing circuitry
detects a fault, the switch is turned off to prevent the fault from passing through the switch or mux to
Page 1 of 8